How to Pick the Right Diamond Cut
Diamond-Cut is the most important property to increase its beauty because a well-cut diamond engagement ring reflects light and facets beautifully.
A poorly cut stone will only reflect what little color it has, making for an unimpressive appearance that can't compete with other stones in terms of brilliance or sparkle, after all, we want our diamonds to be noticed!
Our jewelers' exceptional abilities can be revealed and maximized only by cutting and polishing your beautiful diamond engagement ring with an extremely high level of accuracy that will maximize brilliance in any type or color stone you choose!
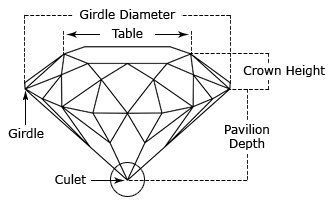
Diamond Anatomy
- Diameter: Width of a diamond measured through the Girdle.
- Table: Largest facet of a gemstone.
- Crown:Top portion of a diamond extending from the Girdle to the Table.
- Girdle:Intersection of the Crown and Pavilion which defines the perimeter of the diamond.
- Pavilion:Bottom portion of a diamond, extending from the Girdle to the Culet.
- Culet:Facet at the tip of a gemstone. The preferred Culet is not visible with an unaided eye (graded “none” or “small”).
- Depth:Height of a gemstone measured from the Culet to the Table.
The cut of a diamond establishes how it reflects light, which is responsible for its sparkle or brilliance. Cut has following three components:
Diamond Cut by Shape
The cut of a diamond establishes how it reflects light, which is responsible for its sparkle or brilliance. Cut has following three components:
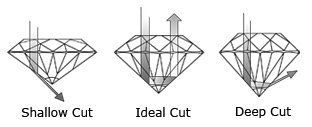
Diamond Cut by Depth
A Diamond Cut by Depth is the ultimate feature for its brilliance and fire.
Shallow Cut:
Shallow Cut will let light lost through a diamond’s bottom causing it to appear dull.
Deep Cut: Deep Cut will allow light to be lost through a diamond’s sides causing it to appear dark.
Ideal Cut:
Ideal Cut is considered as the best cut and it will reflect most or all of the light that enters in the diamond back to the eyes. Quality of a diamond’s cut can be determined on the basis of its power to reflect light.
They can be broadly characterized as Ideal, excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair or Poor. Ideal or Excellent cuts release the inner brilliance of the stone and project maximum amount of fire and sparkle where as Very Good, Good and Fair cuts loose some light that enters the diamond. A poor cut looses most of its light from the diamond sides / bottom and it may even have some “dead” spots inside.
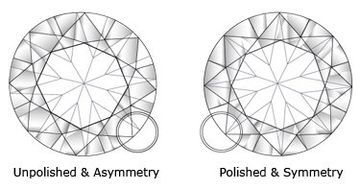
Diamond Polish & Symmetry
Polish and symmetry are two important aspects of the cutting process. The Diamond Polish expresses the smoothness of the diamond’s facets where as the Symmetry refers to alignment of the facets. A poor Diamond Polish, or rough facets, can diminish a diamond’s brilliance, as well as its value.
Color
Diamonds come in every color of the rainbow, from an intense yellow to dark ink-black.
The difference between colors can be minor but it makes a world of difference when grading them for value! A truly "colorless" diamond is rare and considered most valuable because light shines through these stones without obstruction, making their brilliance apparent with only the slightest hint at its pureness.
The most beautiful diamonds are found in trace amounts of yellow or brown. Some sources say that these tints make them more precious, but some people think they mask the stone's brightness and brilliance with their hue. The only way to truly appreciate what color your diamond is without influencing opinion on either side would be by looking at it against a white surface!
| Color Grade | Description | On Unaided Eye Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Colorless | Stone looks absolutely clear and transparent, with no hint of color. | |
| Near Colorless | Stone looks clear and transparent. Color will be noticeable by experts only when compared to diamonds of better grades. | |
| Faint Yellow | Color slightly detectable and will be noticeable by experts only. | |
| Very Light Yellow | Stone shows an increasing yellow tint, even to an untrained eye. | |
| Light Yellow | Stone appears yellow, even to an untrained eye. | |
| Fancy | Bright, remarkable color – usually blue, pink, yellow, Red etc. |
Fancy Colored Diamonds
Although majority of diamonds come in shades of white, there are also “Fancy” natural intensely colored diamonds available in colors like yellow, pink, greens, brown, red, orange, blue etc. These intensely colored diamonds are very rare, attractive and desirable. A deeply colored diamond can cost more than its colorless counterpart. These intensely colored diamonds are known as “Fancy” colored or “Fancies”.
Fancy colored diamonds are graded in two ways. The first factor is the basic hue, such as pink, yellow, blue, green, etc. The second is the intensity. Both color characteristics form the basis for determining a fancy colored diamonds worth. In fancy colored diamonds, Z+ grade is used for their color grading. Usually, the more intense the color, the rarer and more expensive the diamond will be. For example, a fancy light pink diamond costs less than a fancy vivid pink diamond of equal size, shape and clarity. Though fancy colored diamonds rarely occur in nature, laboratories can easily create them through irradiation and heating.
This process can permanently turn a natural colorless diamond into a fancy colored diamond. Treatments have also been developed to make lower-color white diamonds
whiter. Irradiated colored diamonds have a significantly lower value than natural fancy diamonds and can be detected in a gem laboratory.
Fluorescent Diamonds
Fluorescence is a form of illumination that is created when a diamond is exposed to low or high wave ultraviolet radiation. Fluorescence up to some extent is common in majority of diamonds. Faint or medium fluorescence will rarely affect a diamond’s appearance. Usually fluorescence remains unnoticed by human eyes in ordinary light.
Clarity
Clarity is a term used to describe the absence or presence of flaws inside or on the surface of a diamond. In other words, the clarity of a diamond refers to a diamond’s clearness or purity.
When these flaws / marks occur internally, they are called inclusions and the most common types of inclusions include Crystals, Tiny Bubbles representing small minerals that were absorbed into the diamond while it was growing, Internal Graining, Needles, Knots, Chips, Cavities, Cleavage, Feathers, and Clouds. On the contrary, when these flaws / marks occur on the surface, they are known as blemishes and the most common types of blemishes include Polish lines, Naturals, Scratches, Nicks, Pits, transparent stress lines that appear on a diamond’s surface, surface graining, and extra facets, that are usually cut to remove a near-surface inclusion to raise the clarity grade of a stone. Most diamonds have these imperfections in them.
Although many of these flaws are not visible to the naked eye, but under magnification, tiny feather like shapes, crystals, bubbles and dark flecks become noticeable. These slight flaws make every diamond quite unique but they also do affect the beauty and value of the diamond.
Diamond’s clarity is based on the number, size, nature, and location of imperfections on the finished stone. Diamond with higher clarity is more valuable in comparison to diamond that contains numerous inclusions because it is less brilliant due to inclusions interfering with light passing through it.
Diamond Clarity Grading Scale Table
| Clarity Grade Scale | Description | On Inspection through 10x magnification |
|---|---|---|
| F | Flawless | Clear Stone, no inclusions or blemishes. Exceptional and beautiful diamonds. |
| IF | Internally Flawless | No inclusions and only insignificant surface blemishes. Rare and beautiful diamonds. |
| VVS1 – VVS2 | Very, Very Slightly Included – 1 & 2 | Tiny inclusions, which are extremely difficult to find, even under 10x magnifications.An excellent quality diamond. |
| VS1 – VS2 | Very Slightly Included – 1 & 2 | Minor inclusions, which are difficult to see under 10 x magnification. These stonesare less expensive than the VVS1 or VVS2 grades. |
| SI1 – SI2 | Slightly Included – 1 & 2 | Inclusions, which are easy to see under 10 x magnification. A good diamond value. |
| I1 – I2 – I3 | Included – 1, 2 & 3 | Inclusions, which are easy to see under 10 x magnification and sometimes, may be visible with the unaided eye. A good diamond value. Generally I3 grade is not used for jewelry purposes and mostly used in industrial applications. |
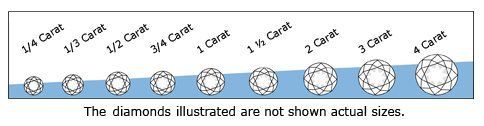
Carat
The term “Carat” refers to the weight of a diamond. It is derived from the carob seeds, which are remarkably consistent in weight and shape and so were the favored scale balances in ancient times. This was standardized in 1907 and after that 1 carat became 0.2 grams or 1/142 of an ounce. Furthermore, each carat is divided into 100 points.
Therefore, ¼ carat diamond is considered as 25 points and ½ carat diamond is considered as 50 points and so on. This term ‘Carat’ is different from the term ‘Karat’ which is used to describe gold’s fineness or purity. When we consider all four Cs, that determine value of diamond, we can find Carat weight most accurately and easily by using a delicately balanced scale capable of weighing extremely small stones.
Diamond’s Carat Weight Scale
The term “Carat” refers to the weight of a diamond. It is derived from the carob seeds, which are remarkably consistent in weight and shape and so were the favored scale balances in ancient times.
This was standardized in 1907 and after that 1 carat became 0.2 grams or 1/142 of an ounce. Furthermore, each carat is divided into 100 points. Therefore, ¼ carat diamond is considered as 25 points and ½ carat diamond is considered as 50 points and so on.
This term ‘Carat’ is different from the term ‘Karat’ which is used to describe gold’s fineness or purity. When we consider all four Cs, that determine value of diamond, we can find Carat weight most accurately and easily by using a delicately balanced scale capable of weighing extremely small stones.
Shape
A Diamond Cut by Shape describes the outline of the stone and pattern of the facet arrangement. Although diamonds are available in various shapes like Round, Princess, Heart, Oval, Pear etc., but when most people think of diamonds, what comes to their mind is the modern round brilliant cut because in jewelry industry, this shape is sold more than 75% of all diamonds. All other non-round shapes are called fancy shapes and these different diamond shapes show individual’s style and personality. The most popular and stylish shapes are defined as under:
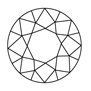
Round Brilliant Cut
The round brilliant cut diamond is the most traditional and popular of all diamond shapes.
This shape maximizes its sparkle because it has 58 facets that offer great brilliance, stability, durability to name just a few things this beautiful stone offers couples who choose them as their engagement ring or wedding band stones!
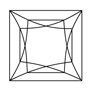
Princess Cut
The Princess Cut is a popular shape for engagement rings.Its beautiful brilliance and unique cut make it one of the most desired stones out there, making this gemstone an excellent choice when looking to propose!
The princess has pointed typically square corners, the ideal ratio should be close to 1:1 length vs width with some variation possible depending on where along that spectrum you fall!
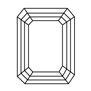
Emerald Cut
The Emerald Cut diamond is a square or rectangular-shaped stone with cut corners.
This shape has 48 to 50 facets that all meet at the top, forming what appears like stairs on either side of an open table for light to pass through more easily than other shapes do.
Emerald-Cut brings less brilliance when compared against fancy ovals and pearls due to its larger look, but this does highlight clarity that can't be beaten!
Oval Cut
The Oval Cut is a beautiful and interesting shape!
The 56 facets provide great brilliance, fire, sparkle to the diamond through its unique form factor that makes it stand out from other types of cuts!
More than any other gemstone does, Oval Cut is an especially radiant stone that can be beyond beautiful when well-cut by professionals!
Marquise Cut
The Marquise Cut is a traditional shape that has elongated ends at both edges.
This shape has 48 to 50 facets that all meet at the top, forming what appears like stairs on either side of an open table for light to pass through more easily than other shapes do.
Emerald-Cut brings less brilliance when compared against fancy ovals and pearls due to its larger look, but this does highlight clarity that can't be beaten!

Pear Cut
The Pear Cut diamond is often called a teardrop due to its single point and rounded end with 56 or 58 facets.
This shape is popular for the uniqueness it brings in addition to brilliance, which makes this an excellent choice if you're looking into pendants or hand jewelry that's small enough for smaller fingers but still large enough on most hands!
Asscher Cut
The Asscher Cut is a modified version of the Emerald.
This shape was named after Joseph Asscher, an ingenious diamond cutter from Holland who developed this new squarer step-cut with an almost octagonal outline in 1902 and patented it as well!
The stone's fire increased due to its extra facets that provided more light reflectance guarantee to sparkle in the sun!
Radiant Cut
The radiant cut is a shape that has been gaining popularity recently because it offers the brilliance of an Emerald with elegance and trimming on its corners.
The diamond-like stones come in various shapes including square or regular rectangles but what sets them apart are those fancy facets found at either side, making this type perfect for adorning your jewelry collection!
Heart Cut
The human heart is the ultimate symbol of love and it's not hard to see why heart
-shaped diamonds are said to be some of our most romantic stones!
The Heart shaped diamond is essentially a pear-shaped diamond with a cleft at the top and it typically contains 59 facets.
With their distinct shapes corresponding directly from how we feel inside, these gorgeous gems can also represent that special someone in your life who has made an impact on yours forevermore!
Baguette Cut
The Baguette Cut diamonds are usually used to fill in channels or stable grooves around an engagement ring's gemstone.
This shape is similar to the Emerald cut, but with more points on either side for stability and less depth overall than its counterpart, making it perfect if you want your stone visible from all angles while not overpowering other facets of her hand!
Trilliant Cut
The Trilliant Cut is one of the unique shapes and it has a very high level of brilliance.
These diamonds may be triangular, square, or heart-shaped with pointed corners for particularly sharp edges that will make your statement heard against any background no matter what you're wearing!
Certificate
This certificate doesn’t state monetary value of a diamond. There are many laboratories available through out the world for diamond certification but below mentioned laboratories are considered as most respected ones in the industry, for their consistency and unbiased diamond grading systems.
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA)
- The Gemological Institute of America was established in 1931 in Los Angeles. The GIA created and introduced the international grading system. Headquarters are still located in Los Angeles.
The Diamond High Council (HRD)
- The Diamond High Council is the officially recognized representative of the Belgium diamond trade and industry. HRD headquarters are located in Antwerp, World Diamond Center.
The American Gem Society Laboratories (AGSL)
- The American Gem Society Laboratories (AGSL) was established in 1934 in Las Vegas, Nevada by Robert M. Shipley, who also established the GIA.
International Gemological Institute (IGI)
- The International Gemological Institute was established in 1975 in Antwerp. This laboratory is also having labs in New York, Bangkok, Mumbai and Tokyo.
- Securing a certificate will provide you a much-needed peace of mind knowing that you are getting your money’s worth. Here are some reasons to buy a diamond along with its certificate:
A diamond certificate gives you the exact details of the stone and on the basis of this information you will be able to do some comparison-shopping before doing the actual purchase.
A diamond certificate allows you to pay money on the basis of stone’s characteristics. Your jeweler wont be able to charge you more and there are very good chances to get the best deals. On resale of diamond along with its certificate, you will get better price for the diamond. To get insurance for your diamond, you also need to produce diamond certificate. It is a standard practice in the Diamond Industry, to ask for a Diamond’s Certificate or Grading Report from the jeweler before the purchase of it.
Diamonds are forever as they are the hardest known substances on earth. But due to our day-to-day activities, it is inevitable that our precious diamond pieces get dirty and soiled. Even they can be scratched, chipped or dulled if not handled correctly. With proper care, they can last a lifetime and can even be handed down as heirlooms to future generations without losing their shining and sparkle. So here are some tips that will help you to preserve the life and beauty of your diamond:
Acquisition of a Diamond or Diamond Jewelry is an important expression of love or accomplishment but on the same time it also represents a major investment of money. It is essential for you to know the credentials of the diamond and obtain confidence in the integrity of what you have acquired. A Diamond Certificate or Diamond Grading Report is a statement, issued by an independent Gemological Laboratory, that at the time of evaluation, the diamond in question has been examined, measured, and scrutinized by experienced Diamond Graders, using various gemological instruments, and determined to contain the characteristics as stated in the Certificate or Report. In other words, a diamond certificate can be accurately described as the blueprint of a diamond. This Certificate or Report includes an analysis of the diamond’s characteristics in an easy to understand format.
Generally a certificate or report covers following characteristics of a diamond along with the laboratory and certificate details:
- Name of the Laboratory
- Certificate Number
- Shape and Cutting Style
- Measurements of the Diamond’s diameter
- Carat Weight
- Color Grade
- Clarity Grade
- Cut Grade
- Finish, Polish & Symmetry
- Fluorescence
- Comments
- Plotted diagram of the diamond for the imperfections.
- Key to Symbols that helps us to identify characteristics marked in the plot.
- Security Features for the Certificate
- Graphical image of Diamond Structure
- Information about Diamond’s Depth, Table, Girdles, Culet and Facets etc.
This certificate doesn’t state monetary value of a diamond. There are many laboratories available throughout the world for diamond certification but below mentioned laboratories are considered as most respected ones in the industry, for their consistency and unbiased diamond grading systems.
A diamond certificate gives you the exact details of the stone and on the basis of this information you will be able to do some comparison-shopping before doing the actual purchase. A diamond certificate also allows you to pay money on the basis of stone’s characteristics. Your jeweler wont be able to charge you more and there are very good chances to get the best deals.
On re-sale of diamond along with its certificate, you will get better price for the diamond.
To get insurance for your diamond, you also need to produce diamond certificate. It is a standard practice in the Diamond Industry, to ask for a Diamond’s Certificate or Grading Report from the jeweler before the purchase of it.
Diamonds are forever as they are the hardest known substances on earth. But due to our day-to-day activities, it is inevitable that our precious diamond pieces get dirty and soiled. Even they can be scratched, chipped or dulled if not handled correctly. With proper care, they can last a lifetime and can even be handed down as heirlooms to future generations without losing their shining and sparkle. So here are some tips that will help you to preserve the life and beauty of your diamond:
Cleaning of Diamond Jewelry
Regular cleaning of Diamond Jewelry is essential to maintain the shine and brilliance of diamonds.
When wearing them, they get dirty as you use various skin and body care regimens such as soaps, lotions, and even our skin’s natural oils. When you are not wearing them they collect dust, use a small soft brush such as an eyebrow or lipstick brush, soap, and water to clean your diamond jewelry.
If you feel that your diamond jewelry requires a stronger cleansing then you can use a solution of one part ammonia and six parts water for cleaning the diamonds. It is also a good idea to have them cleaned once a year by a professional jeweler, where he will check the security of the settings.
Storing of Diamond Jewelry
Storing of diamond jewelry is also important as a diamond can scratch another diamond, as well as other jewelry pieces. Storage of diamond jewelry needs following precautions:
- Diamond jewelry should be stored individually in a soft cloth pouch to ensure that a diamond should not scratch other diamonds or other jewelry.
- Diamond jewelry pieces are best stored in a fabric-lined jewel case or in a box with compartments or dividers.
- You should not wear diamond jewelry while doing heavy work. Even though a diamond is extremely durable, it can be chipped by a hard blow, and even everyday activity can loosen jewelry setting.
- You should avoid the situation where your diamonds come in contact with chlorine bleach, hair spray or other chemicals because they can pit or discolor the mounting.If you will follow the above mentioned caring tips then your diamond jewelry will always shine and sparkle likes a new one.
Location
J&H Diamond Jewelers
5118 Old Springville Rd.
Pinson, AL 35126
Contact Us
(205) 853-4121
All Rights Reserved | J&H Diamond Jewelers
